Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a prevalent oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to gum inflammation, gum recession, tooth loss, and even impact overall health.
Periodontal disease is a serious condition that requires the expertise of a dental professional. A periodontist will assess the severity of the disease, develop a personalized treatment plan, and provide ongoing care to restore your oral health.
How does the Periodontal Disease develop?
Periodontal disease (or gum disease) is an inflammatory condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not removed through proper oral hygiene practices, plaque can harden into tartar, which provides a breeding ground for bacteria.
The bacteria in plaque and tartar release toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation. This initial stage of gum disease is called gingivitis. Symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, as well as persistent bad breath. At this stage, the damage is mostly reversible with proper dental care.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced stage of gum disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Periodontal disease can be caused by a combination of factors. Here are some common causes and risk factors associated with the development of periodontal disease:
1. Poor oral hygiene – Inadequate oral hygiene practices, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, can lead to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums.
2. Plaque and tartar build-up – If not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar (calculus), which cannot be removed by brushing alone. Tartar provides a rough surface for more plaque to adhere to, leading to further gum irritation.
3. Tobacco use – Smoking or using other tobacco products is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease. Tobacco use weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off bacterial infection. It also impairs blood flow to the gums, slowing down the healing process.
4. Genetics – Some individuals may be more genetically predisposed to developing periodontal disease. Certain genetic variations can affect how the immune system responds to the bacteria in plaque, making some people more susceptible to inflammatory diseases and damage.
5. Hormonal changes – Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This can increase the risk of developing gum disease.
6. Diabetes – Diabetes affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing infections, including gum disease. Conversely, gum disease can also make blood glucose control more challenging, leading to complications in managing diabetes.
7. Medications – Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, anticonvulsant, and immunosuppressants, can affect gum health and increase the risk of gum disease. It is important to inform your dentist or periodontist about any medications you are taking or your medical history.
8. Poor nutrition – A diet lacking essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C and antioxidants, can weaken the immune system and impair gum health. Nutritional deficiencies can make the gums more susceptible to infection and hinder the healing process.
9. Stress – Chronic stress can harm the immune system, making it harder for the body to combat infections, including gum disease. Additionally, stress may lead to unhealthy coping habits like smoking or neglecting oral hygiene.
10. Age – As individuals age, they may be more susceptible to gum disease due to natural wear and tear on the gums and teeth over time. However, gum disease can affect people of all age groups.
Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, can exhibit various warning signs and symptoms that indicate the presence and progression of the condition. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
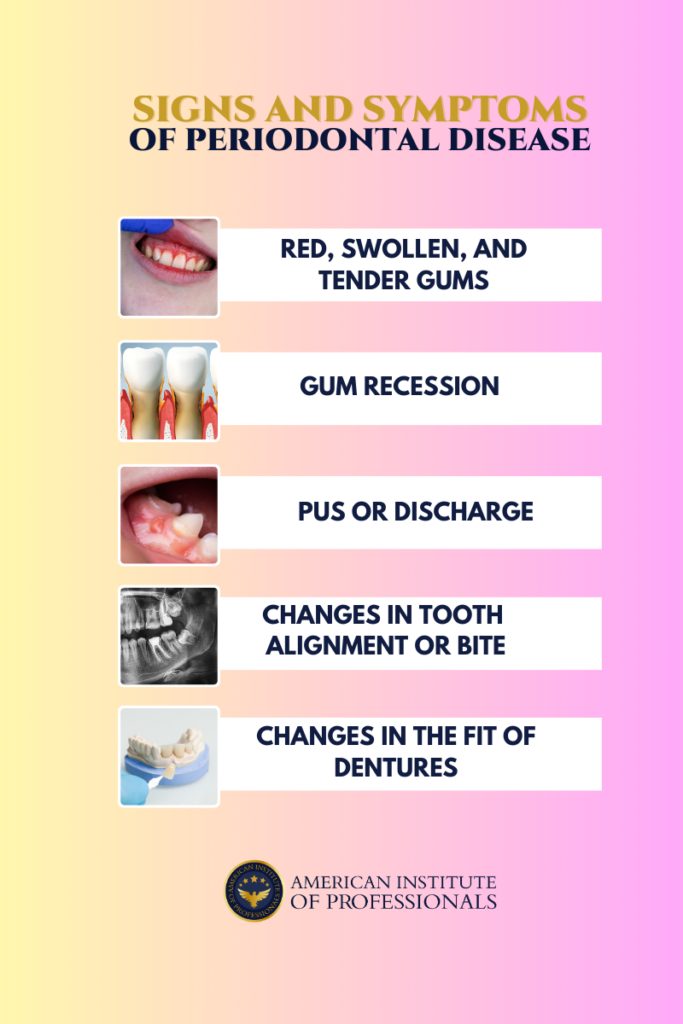
Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment Options
Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment options for periodontal disease involve a comprehensive approach to assess the extent of the disease and provide appropriate care. Here’s an overview of the process:
Diagnosis
- Visual examination – A periodontist visually inspects your gums, checking for signs of inflammation, recession, bleeding, and other symptoms associated with gum disease.
- Probing – Using a small dental instrument, the depth of gum pockets is measured. Healthy pockets are usually shallow, while deeper pockets indicate gum disease.
- X-rays – Dental X-rays may be taken to evaluate the bone structure supporting the teeth and identify any bone loss associated with periodontal disease.
Evaluation
- Scaling – This process involves removing plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gum line through scaling. It helps eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Root planing – Root surfaces are smoothed to discourage bacterial attachment and facilitate gum tissue reattachment.
Treatment
- Antibiotics – In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection and promote healing.
- Antiseptic mouthwash – Recommended for reducing bacteria and controlling infection.
- Flap surgery – In advanced cases, a periodontist may perform flap surgery to lift the gums and gain access to the tooth roots for deep cleaning and removal of bacteria.
- Bone and tissue grafts – If significant bone or gum tissue loss has occurred, grafting procedures may be required to regenerate and restore the supportive structures.
- Regular check-ups – Follow-up visits are crucial to monitor the progress of treatment, assess the health of your gums, and make any necessary adjustments.
- Oral hygiene practices – Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and antimicrobial mouthwash use, is essential to maintain gum health and prevent further disease progression.
Finding the Right Periodontist
Hiring a periodontist offers several advantages when it comes to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of periodontal disease. Here’s why you should consider hiring a periodontist:
1. Specialized expertise – Periodontists are dental specialists who have undergone extensive training beyond dental school to focus specifically on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum diseases.
2. Advanced treatment options – Periodontists are skilled in performing a wide range of advanced periodontal procedures. From non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing to surgical interventions such as gum grafting, bone regeneration, and dental implant placement, they possess the expertise to offer the most suitable and effective treatment options for your specific needs.
3. Comprehensive approach – Periodontists can develop personalized treatment plans that address the underlying causes of gum disease, considering factors such as bone health, bite alignment, and overall oral hygiene.
4. Early detection and intervention – Periodontists have the skills to detect and diagnose gum disease in its early stages, often before it becomes symptomatic or progresses to a more severe form. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can help prevent further damage to the gums and supporting structures, potentially saving teeth from being lost.
5. Periodontal surgical expertise – Periodontists are trained in performing these surgical procedures with precision and expertise, ensuring optimal results and improved oral health outcomes.
6. Long-term maintenance – Periodontists can develop long-term treatment plans, provide regular check-ups, and offer guidance on oral hygiene practices and preventive measures to help you maintain healthy gums and prevent disease recurrence.
7. Collaborative care – Periodontal disease can be interconnected with other dental and overall health issues. Periodontists often collaborate with other dental specialists, such as orthodontists or prosthodontists, to develop comprehensive treatment plans that address multiple aspects of oral health.
By entrusting your oral health to a skilled periodontist, you can improve the outcomes of your periodontal treatment and enjoy a healthier, more confident smile.
Hire a Skilled Periodontist Today!
Take control of your periodontal health and hire a qualified periodontist today. Don’t wait any longer – schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a healthier smile.





